Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mihara, Morihiro; ; Ueta, Shinzo*; *
JNC TN8430 99-011, 27 Pages, 1999/11
In radioactive waste disposal, compacted Na-bentonite has been proposed for a buffer material. However, Na-bentonite would change to Ca-bentonite in the long term period. The change of Na-bentonite to Ca-bentonite might cause the change in the data concerning with nuclides migration properties such as permeability, sorption and diffusion. In this study, effective diffusion coefficients of HTO, Cs, I and C in compacted Ca-bentonite which was changed from Na-bentonite, Kunigel V1, were obtained and were compared to published those of Kunigel V1. In addition, effective diffusion coefficients for compacted Ca-bentonite with syncetic sea system water, SW, were obtained in order to investigate effect of solution composition. The magnitude of effective diffusion coefficients in Ca-bentonite are arranged in smaller order as Cs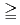 HTO
HTO I
I C. It is estimated that their effective diffusion coefficients are same those of Na-bentonite. About effect of solution composition, effective diffusion coefficients of HTO in 1.8g/cm
C. It is estimated that their effective diffusion coefficients are same those of Na-bentonite. About effect of solution composition, effective diffusion coefficients of HTO in 1.8g/cm dry density with SW were almost same values with distilled system water, DW. However, effective diffusion coefficients of HTO in lower density were smaller than values with DW. Regarding as effective diffusion coefficients of Cs in 1.8g/cm
dry density with SW were almost same values with distilled system water, DW. However, effective diffusion coefficients of HTO in lower density were smaller than values with DW. Regarding as effective diffusion coefficients of Cs in 1.8g/cm dry density, the effect of SW could not be observed as well as HTO. However, effective diffusion coefficients of I and C existing as an anion in pore water of bentonite increased by the reduction in the ion exclusion.
dry density, the effect of SW could not be observed as well as HTO. However, effective diffusion coefficients of I and C existing as an anion in pore water of bentonite increased by the reduction in the ion exclusion.
G M N BASTON*; J A BERRY*; M BROWNSWORD*; D J LLETT*; C M LINKLATER*; S W SWANTON*; Tweed, C. J.*
JNC TJ8400 99-078, 72 Pages, 1999/03
A desk study has been carried out to establish the feasibility of measuring the oxidation state of plutonium under near-neutral strongly-reducing conditions. X-ray absorbance spectroscopy appears to be capable of establishing the oxidation state of plutonium sorbed on a suitable substrate. An experimental and modelling investigation has been performed to study the sorption of plutonium onto basalt, mudstone and sandstone under strongly-reducing conditions at three concentrations of carbonate. Appropriate synthetic rock-equilibrated de-ionised water and seawater were used. A model has been developed to describe the sorption of plutonium onto basalt, mudstone and sandstone in de-ionised water and seawater. Predicted R values are generally in good agreement with the observed experimental measurements. The model is based on sorption of plutonium(III) species and assumes iron oxide is the dominant sorbing phase.
values are generally in good agreement with the observed experimental measurements. The model is based on sorption of plutonium(III) species and assumes iron oxide is the dominant sorbing phase.
Kurasawa, T.; ; ;
JAERI-M 86-152, 81 Pages, 1986/10
no abstracts in English
Kaetsu, Isao; ; ; *
Journal of Polymer Science; Polymer Chemistry Edition, 11(6), p.1149 - 1156, 1973/06
no abstracts in English